Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
| 제품번호 | 종 | 제품 설명 | 구조 | 순도 | 특징 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPR-H52H4 | Human | Human Erythropoietin R / EPO R Protein, His Tag (MALS & SPR verified) |  |
|
|
| ERR-H5253 | Human | Human Erythropoietin R / EPO R Protein, Fc Tag (MALS verified) |  |

|
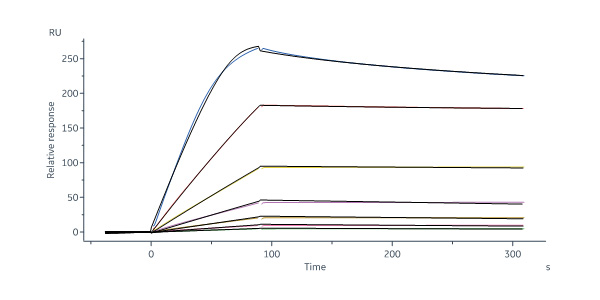
Human Erythropoietin R Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. EPR-H52H4) immobilized on CM5 Chip can bind Human EPO Protein, premium grade (Cat. No. EPO-H4214) with an affinity constant of 0.142 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore 8K) (QC tested).
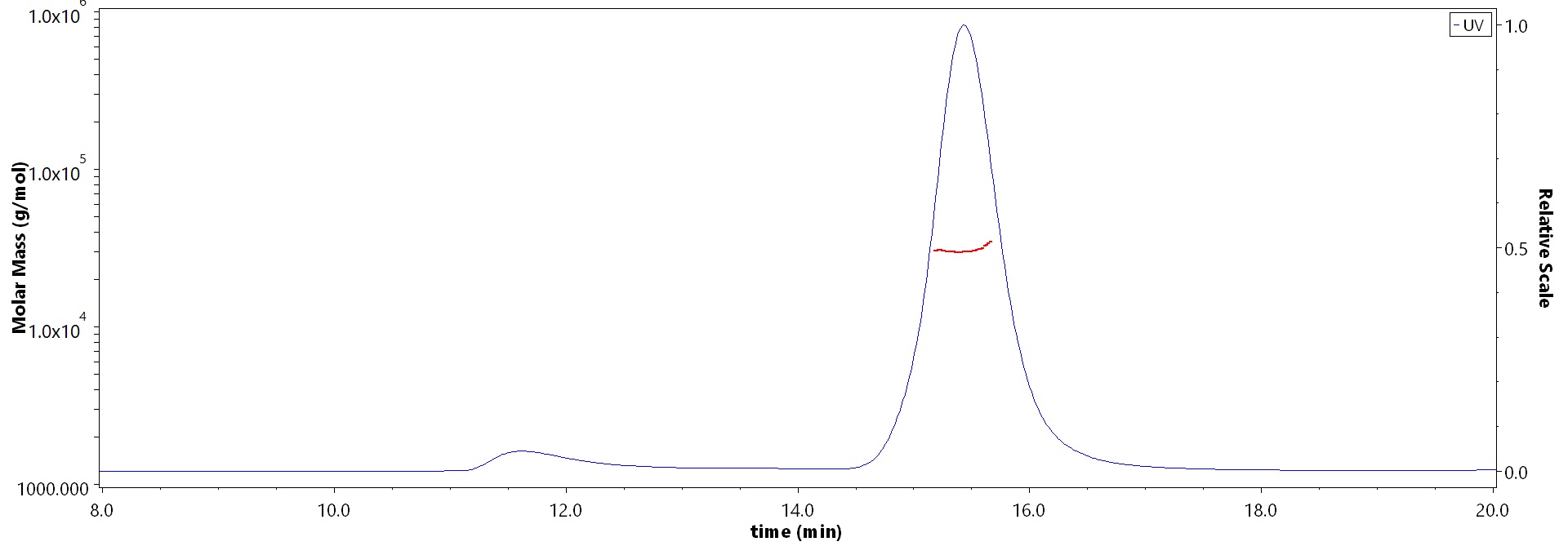
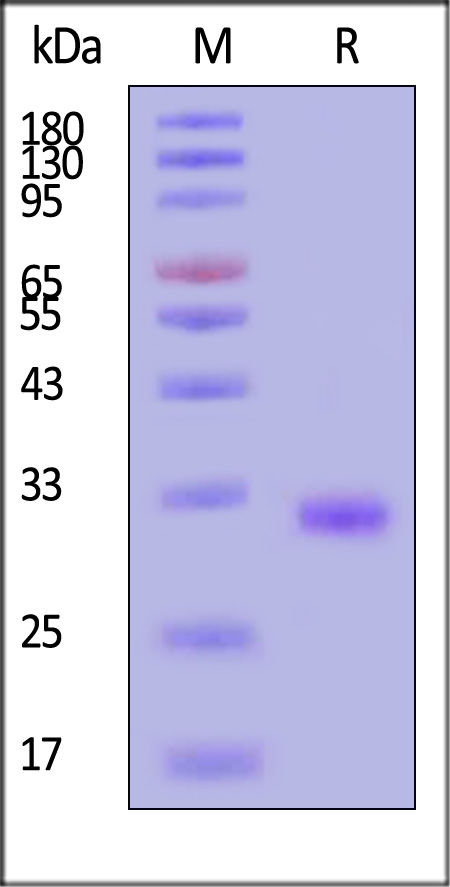
The purity of Human Erythropoietin R Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. EPR-H52H4) is more than 85% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 25-38 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.